The difference between null and undefined in JS is:
undefined usually means that a variable has been declared but not defined.
While null is used to indicate that a variable intentionally has no value.
In JavaScript, null and undefined are both values that represent absence of a meaningful value, but they have slightly different meanings.
Undefined
null and undefined in javascript
undefined in JavaScript represents a variable that has been declared but has not been assigned a value yet, or a property that does not exist in an object.
It is a primitive value that is automatically assigned to variables that have just been declared or to function parameters that have not been provided with a value.
Example:
let x;
console.log(x); // Output: undefinedNull
null and undefined in javascript
null is a special value in JavaScript that represents the intentional absence of any object value.
It is typically used to explicitly indicate that a variable or object property does not have a value, or to reset a variable to no value.
Example:
let y = null;
console.log(y); // Output: nullNull vs Undefined: Pros and Cons
null and undefined in javascript
A table summarizing the pros and cons of using null and undefined in JavaScript:
| Null | Undefined | |
|---|---|---|
| Pros | Explicitly indicates absence of value | Automatically assigned to uninitialized variables |
| Can be used to reset a variable to no value | Automatically assigned to missing object properties | |
| Useful for checking if a variable has been intentionally set to no value | ||
| Cons | Requires explicit assignment to use | Can be confusing when encountered unexpectedly |
| May be used inconsistently | Can lead to bugs if not handled properly | |
| Cannot be used to distinguish between missing and uninitialized properties in objects | ||
Bottom line
null and undefined in javascript
The bottom line is to use null when you want to explicitly indicate the absence of a value, or when you need to reset a variable to no value.
Use undefined for variables or object properties that have not been initialized or do not exist yet
What to do next?
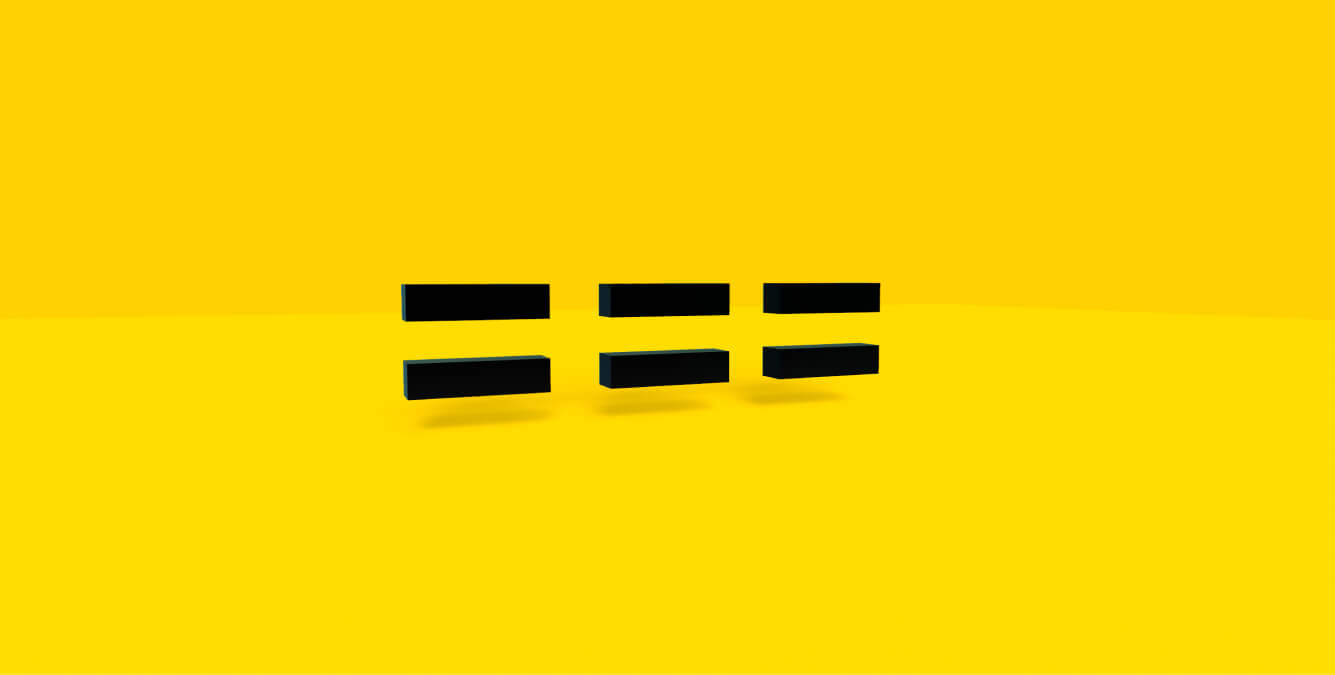
See Javascript Question #2: “What is difference between == and === in JS?“